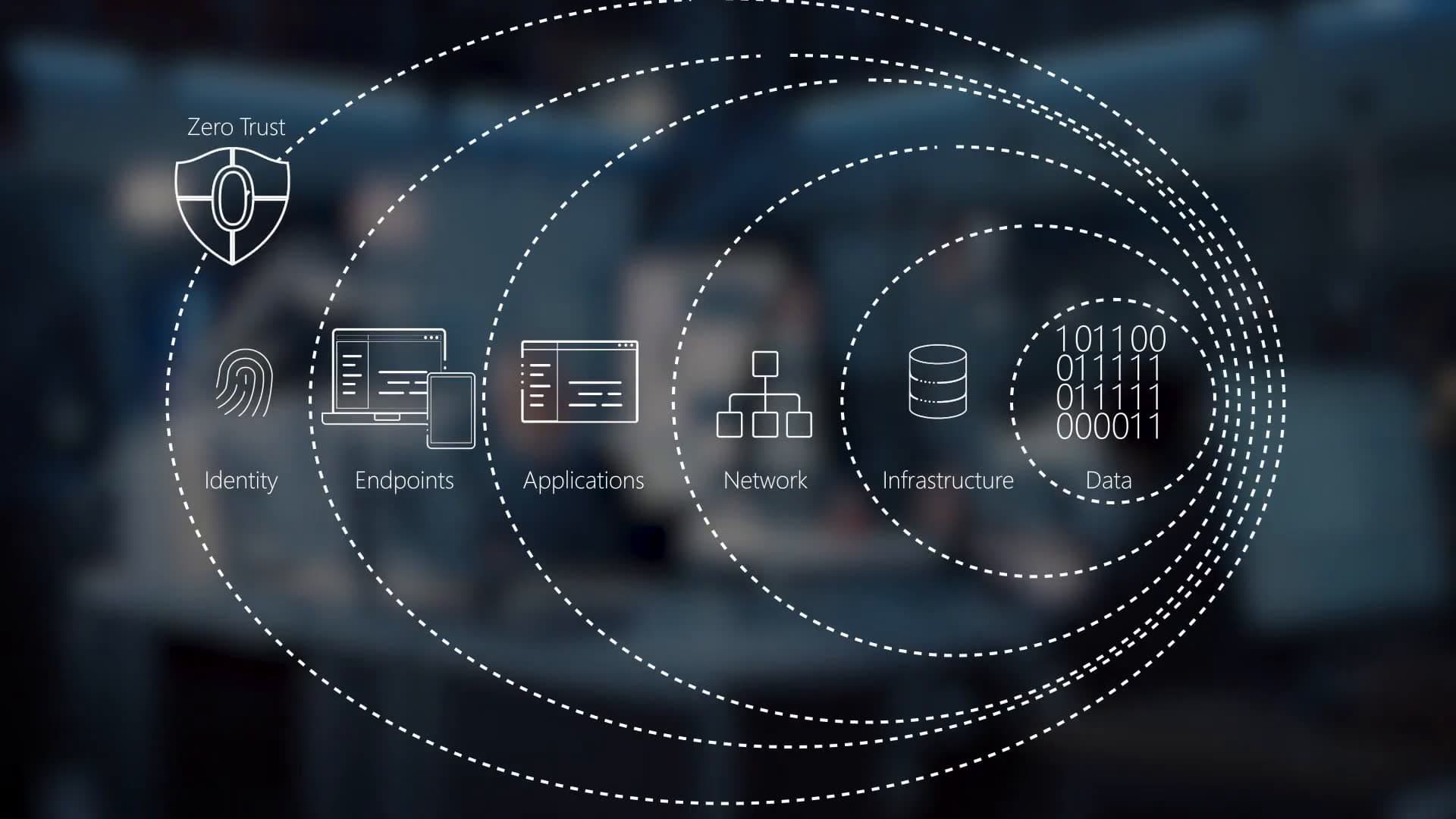
The traditional "castle and moat" security model is dead. In an era where data lives in the cloud, employees work from anywhere, and IoT devices proliferate, the concept of a "perimeter" has dissolved. Welcome to the age of Zero Trust.
The Paradigm Shift
Zero Trust is not a product; it's a strategy. It operates on a simple, yet radical premise: trust nothing, verify everything. Every user, device, and application attempting to access resources must be authenticated and authorized, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the corporate network.
Core Pillars of Zero Trust in 2026
- Identity Governance: Moving beyond passwords to adaptive, biometric, and behavior-based authentication.
- Micro-segmentation: Breaking down networks into granular zones to contain breaches and prevent lateral movement.
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time analysis of user behavior and device health to detect anomalies before they become threats.
The Business Case
Implementing Zero Trust is not just about security; it's about business agility. By decoupling access from physical location, organizations can securely empower a global workforce, accelerate cloud adoption, and safely integrate third-party partners. It turns security from a blocker into an enabler of innovation.
Implementation Challenges
Transitioning to Zero Trust is a journey, not a flip of a switch. It requires a cultural shift, legacy system modernization, and comprehensive data classification. However, the cost of inaction is far greater. In 2026, Zero Trust is not just best practice—it is the baseline for survival.
Published on Oct 12, 2025